Experts in hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer have gathered.
"We do not give up on cancer treatment."
Hepatitis, Cirrhosis, and Liver Cancer
The Current Status of Liver Cancer
- In Japan, the number of deaths due to liver cancer exceeds 30,000 annually, ranking fourth in men and sixth in women in terms of mortality.
- Liver cancer has been considered a difficult-to-detect cancer with poor prognosis, but advances in treatment have been made since the implementation of the Basic Act on Hepatitis Countermeasures.
What is Hepatitis and Cirrhosis
- Hepatitis:
A disease where inflammation occurs in the liver due to infection with hepatitis viruses. Symptoms such as general fatigue and loss of appetite may occur, but many cases are asymptomatic. It should be considered as a "high-risk group for liver cancer" and managed accordingly. - Cirrhosis:
A disease where chronic hepatitis progresses, leading to the destruction of liver cells followed by the deposition of fibrous tissue, causing the liver to become hardened. Symptoms such as edema, ascites, and jaundice appear as it progresses. Prolonged cirrhosis increases the risk of liver cancer significantly.
The Causes of Hepatitis and Cirrhosis
Most cases of hepatitis are caused by infection with hepatitis viruses, but fatty liver hepatitis due to excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, diabetes, and other factors can also be causes.
Treatment for Hepatitis and Cirrhosis
Antiviral drug therapy is crucial for viral hepatitis and cirrhosis. Adrenal cortical steroids are used for autoimmune hepatitis, while abstinence from alcohol, dietary therapy, and exercise are important for fatty liver hepatitis.
Cell-free and Concentrated Ascites Reinfusion Therapy (CART) is a treatment for refractory ascites. This method involves extracting ascites fluid from the abdomen, filtering and concentrating it, and then reinfusing protein components and other substances back into the patient's body.
Key Features of KM-CART Method
- Complete Processing:
All ascites fluid is drained and fully processed. - Membrane Cleaning System:
Unlike traditional CART methods that had limitations on the amount of ascites fluid that could be processed, the KM-CART method employs a membrane cleaning system that allows for rapid and large-volume processing even with easily clogged ascites fluid. - High Effectiveness:
By processing large amounts of ascites fluid and infusing a significant amount of proteins via intravenous drip, each treatment session yields a high therapeutic effect.
Achievements
CART treatment began in 2010, with the introduction of the KM-CART method in 2017. From 2017 to 2021, there were approximately 640 cases treated with KM-CART. The maximum processed ascites fluid volume per case was approximately 18 liters, with an average processed volume of about 7 liters.
Treatment Schedule
- The treatment typically spans 2 nights and 3 days.
- On the first day, preoperative examinations are conducted, CART treatment is administered on the second day, and discharge occurs on the third day after confirming blood test results.
- CART is an insurance-covered treatment and can be received once every two weeks.
- To undergo treatment, patients must first consult their primary care physician and make an appointment for examination with a medical information release form.
The KM-CART method is an advanced approach to effectively treating refractory ascites, contributing to symptom relief in patients by processing large volumes of ascites fluid.
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Diagnosis
- Blood Tests:
Examining liver function and virus-related markers. - Imaging Diagnosis:
Using ultrasound, CT scans, MRI, etc., to evaluate the presence and condition of hepatocellular carcinoma.
ーUltrasound is non-invasive and useful for screening.
ーCT scans show intense staining in the early phase and low absorption in the late phase for typical hepatocellular carcinoma.
ーMRI is particularly effective with gadolinium contrast agents or liver-specific contrast agents in dynamic MRI. - Tumor Markers:
Markers like AFP (Alpha-Fetoprotein) and PIVKA-II serve as indicators of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment
There are various treatment methods for hepatocellular carcinoma, tailored to the tumor's characteristics and the patient's liver function.
| Liver Resection: | ・Surgically removing the cancerous part of the liver. ・Provides reliable local control but can be highly invasive and not suitable for poor liver reserve. |
| Percutaneous Treatments: | [Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)] ・Using high-frequency electrical currents to coagulate and necrotize the tumor. ・Effective for tumors smaller than 3 cm and less invasive than surgery. [Ethanol Injection Therapy (PEIT)] ・Injecting ethanol into the tumor to induce tumor cell necrosis. ・Applicable to small tumors like RFA and allows for repeated treatments. |
| Transarterial Embolization Therapy (TAE/TACE): | ・Injecting embolic materials or anticancer agents into the tumor's nutrient blood vessels to induce necrosis. ・Extends survival, but not suitable for poor liver reserve. |
| Transarterial Infusion Chemotherapy (TAI): | ・Directly administering chemotherapy drugs into the hepatic artery. ・Used when TACE is not possible or for tumors with advanced portal vein thrombosis. |
| Systemic Chemotherapy: | Administered for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma or cases with distant metastasis. |
| Liver Transplantation: | ・Applicable if the tumor meets the Milan criteria. ・Includes deceased donor liver transplantation and living donor liver transplantation from relatives. |
| Radiation Therapy: | Proton beam therapy and heavy particle therapy are promising, but not yet established as standard treatments. |
Hepatocellular carcinoma treatment involves utilizing these methods individually or in combination based on tumor characteristics and patient liver function. Treatment advancements in hepatitis are crucial for controlling hepatocellular carcinoma progression, leading to improved treatment outcomes in digestive system cancers.

At Kurume Chuo Hospital, we provide various treatment options tailored to each patient's needs as professionals in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. Feel free to consult us with any questions or concerns regarding liver-related issues.
Regenerative Medicine
At Kurume Chuo Hospital, regenerative medicine using autologous adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells is being conducted.
- Autologous Adipose Stem Cell Transplantation for Liver Cirrhosis (Project Number PB7190016)
- Fat Stem Cell Transplantation Therapy for Chronic Pain (Project Number PB7180024)
These treatments are self-pay services and are implemented based on approved treatment plans by the Health Bureau. Mesenchymal stem cells have immunomodulatory abilities and minimal rejection responses, leading to their differentiation potential into liver cells and nerve cells, contributing to liver fibrosis suppression and nerve regeneration.
Stem Cell Therapy for Liver Cirrhosis
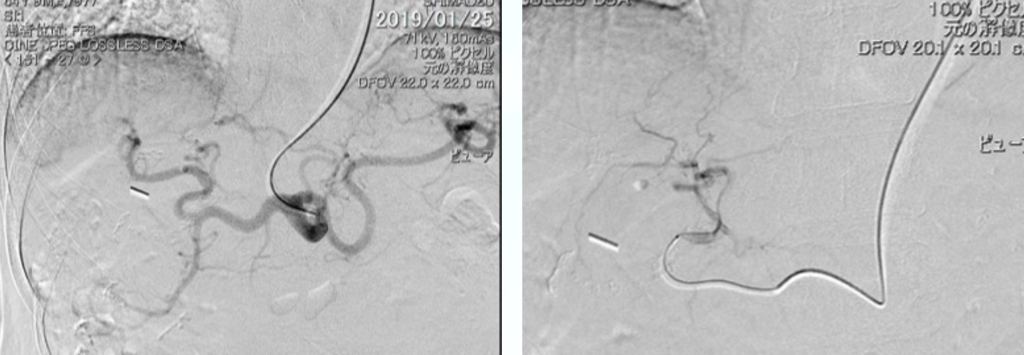
Autologous adipose stem cell transplantation for liver cirrhosis is administered as an outpatient procedure through the left brachial artery puncture. After administering 20cc of stem cells through the hepatic artery, patients can return home the same day after 2 hours of rest. The treatment is performed three times over six months to observe improvements in liver cirrhosis.
A study presented at the 2020 Liver Congress reported a trend of Child-Pugh score reduction in 8 cases, showing promise as an effective treatment for liver cirrhosis.
Stem Cell Therapy for Chronic Pain
Stem cell transplantation therapy for chronic pain is administered for conditions like muscle pain, bone pain, joint pain, neuropathic pain, regardless of the underlying disease. The treatment is delivered via approximately 1-hour intravenous infusion, allowing patients to return home the same day.
This treatment has shown a high improvement rate of over 80% in pain relief, with reported cases of patients previously unable to walk becoming able to practice walking again.
Treatment Procedure
Under local anesthesia, subcutaneous fat is collected from the abdomen. The incision is approximately 1.5 cm.
The collected cells are transported to a cell culture processing facility on the same day. They are cultured for over 50 days to reach over 50,000,000 cells.
Administered at Kurume Chuo Hospital.
Stem cell therapy, as part of regenerative medicine, is evolving as a new treatment option for specific diseases. Particularly, using autologous adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells minimizes rejection reactions and has the potential for application in various disease treatments.
Prices
※ The treatment and costs for hepatitis, cirrhosis, and cancer depend on the patient's condition. For detailed pricing, please consult directly with the physician during the examination.
Stem Cell Therapy for Liver Cirrhosis
¥2,860,000 to ¥3,146,000+ additional fees.
Additional fees may apply depending on the situation.
Stem Cell Therapy for Chronic Pain
¥2,860,000 + additional fees Additional fees may apply depending on the situation.
Hospital Information
| Name of Medical Institution | Medical Corporation Itano Kai Kurume Chuo Hospital |
| Address | 2-3-8 Komorino, Kurume City, Fukuoka Prefecture 830-0001, Japan |
| Access | [Bus] Get off at the Kyushu Institute of Technology bus stop on Nishitetsu Bus Kurume Kosei and walk for 5 minutes. [Car] 20 minutes from Kyushu Expressway Kurume Interchange |
| Operation Hours | Monday to Friday 9:00-12:00/14:00-17:00 Saturday 9:00-12:00 (Closed on Sundays, public holidays, and the 2nd, 4th, and 5th Saturdays of the month.) |
| Website | https://www.kurume-chuo.jp/ |
